Guide to IoT protocols
Follow are the popular IoT protocols these days
1. MQTT
2. CoAP
Introduction for MQTT and example
Nowadays we hear a lot about MQTT with IoT based projects. Let's see actually what is MQTT with simple examples in your Pc and later you can use them for your future IoT projects.
MQTT is a publish/subscribe protocol that allows edge-of-network devices to publish to a broker. Clients connect to this broker, which then mediates communication between the two devices. Each device can subscribe, or register, to particular topics. When another client publishes a message on a subscribed topic, the broker forwards the message to any client that has subscribed.
Hey let's make the idea so simple
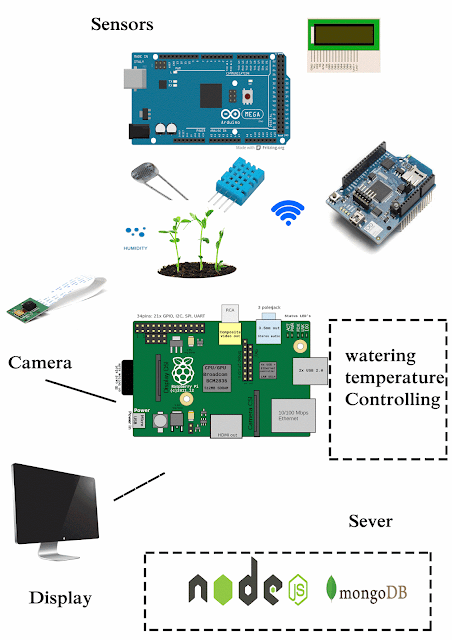
As an example imagine you have a plant. You put 3 sensors to it
temperature sensor, humidity sensor, light intensity sensor
So you need to get these sensor data to your application. Let's use the MQTT protocol to this scenario.
Here we create topics to each sensor
a message broker is a software we have to install to do this stuff. There are many brokers. here I'm using the mosquitto broker
http://mosquitto.org/
eg:-
temperature sensor plant/temp
humidity sensor plant/hum
light intensity sensor plant/light
So these are the topics about each sensor. All the sensor data will be published to these topics in the broker.
So let's move to the client part
The client has to subscribe to these topics to get data from the sensors.
simple they can subscribe to these topics
How to Install in your machine?
Linux
Windows
http://www.eclipse.org/mosquitto/download/
Let's move to the practice?
eg
In separate terminal windows do the following:
plant/temp sensor_val this is how MQTT works simply The MQTT protocol allows your SCADA system to access IIoT data. MQTT brings many powerful benefits to your process:
How Does MQTT Work?MQTT is a publish/subscribe protocol that allows edge-of-network devices to publish to a broker. Clients connect to this broker, which then mediates communication between the two devices. Each device can subscribe, or register, to particular topics. When another client publishes a message on a subscribed topic, the broker forwards the message to any client that has subscribed.MQTT is bidirectional and maintains stateful session awareness. If an edge-of-network device loses connectivity, all subscribed clients will be notified with the “Last Will and Testament” feature of the MQTT server so that any authorized client in the system can publish a new value back to the edge-of-network device, maintaining bidirectional connectivity. The lightweights and efficiency of MQTT makes it possible to significantly increase the amount of data being monitored or controlled. Prior to the invention of MQTT, approximately 80% of data was being left at remote locations, even though various lines of business could have used this data to make smarter decisions. Now MQTT makes it possible to collect, transmit, and analyze more of the data being collected. Who Uses MQTT?MQTT was originally developed for the low-bandwidth, high-latency data links used in the oil and gas industry. However, MQTT is now used in many applications beyond oil and gas — from controlling smart lighting systems to the Facebook Messenger application. Amazon Web Services recently announced that Amazon Internet of Things (IoT) is based on MQTT, as well. Overall, MQTT appears to be the protocol best suited for the control systems used by industrial organizations, and we can expect that its rapid rate of adoption will only increase in the future.So i think now you have a good idea about mqtt. Hope your projects will be more fascinated with mqtt. |



Comments
Post a Comment
Comment